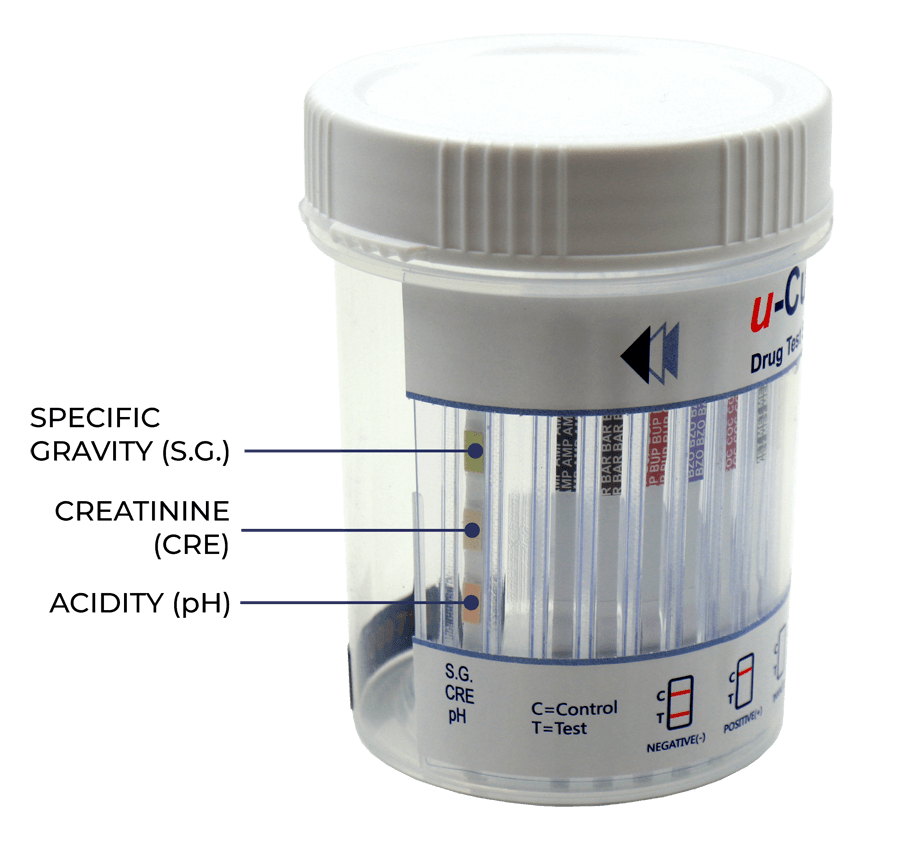
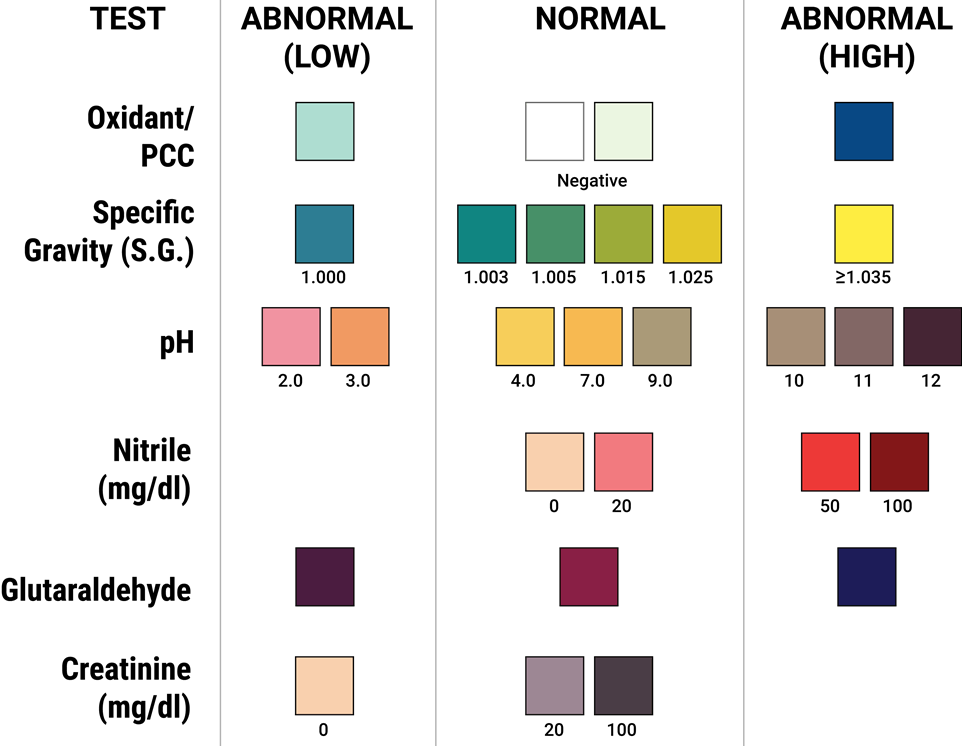Adulterants are substances added to drug tests, directly to the sample or by ingestion, to prevent detection of a drug. UCP Biosciences can configure u-Cups with up to six different adulterant tests, including (1) oxidant/PCC, (2) specific gravity (S.G.), (3) pH, (4) nitrile, (5) glutaldehyde (GLUT), and (6) creatinine (CRE).